The metaverse is undoubtedly stretching the limits of our digital capabilities as the physical and digital worlds collide. The virtual reality (VR) of the metaverse allows for whole new interactions, controls, and experiences with everything from human identity, personality, and reputation to assets, emotions, and history.
What is metaverse?
Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), gaming, social engagement, and commerce all converge in the metaverse, a virtual universe that stands in for a new frontier, to produce experiences that span the actual and virtual worlds. For this reason, a lot of people consider the metaverse and related Web3 technologies, like the blockchain, NFTs, cryptocurrencies, and decentralized computation, to be the beginning of a new internet. What is in store for users in the metaverse? access to professional prospects, compelling virtual social and personal experiences, and solutions to numerous physical restrictions.
Seven layers of the metaverse
1. Experience
A lot of people consider of the metaverse as a 3D space that surrounds us. However, the metaverse isn’t 3D or 2D or even graphic; it’s about the unstoppable dismaterialization of physical space, distance and objects.
The constraints that physically imposes might no longer be present in physical space as a result of the metaverse dematerializing it. The metaverse’s VR has the potential to give experiences that the physical world will never be able to.
2. Discovery
Discovering is all about the pull and pull that exposes people to different experiences. It is a huge ecosystem and an area that is of the most profitable for various businesses — including many of the most significant in the global marketplace. In general, the majority of discover platforms can be classified as either inbound (the person is actively looking for information regarding the event) as well as inbound (marketing that wasn’t specifically asked for by the person or even in the event that they opt in).
3. Creator economy
To create and develop tools, apps, or asset markets on earlier iterations of the internet, innovators needed to have some level of programming expertise. Nowadays, developing online applications is possible without coding thanks to web application frameworks. As a result, there are ever more designers and artists on the internet.
Everyone will soon be able to create content on the internet without needing to spend hours studying programming. The economics of Web 3.0, or the creative era, is defined by this sharp increase in the number of creators.
4. Spatial computing
With virtual assistants and ride-hailing applications, spatial computing has already made our lives easier. By enabling customers to try on clothing in virtual changing rooms, it has made fashion enjoyable and buying more convenient. You will soon be able to work, shop, and interact as avatars in a detailed, three-dimensional digital environment that closely resembles the actual one thanks to spatial computing.
More than ever, we are able to combine the virtual and real worlds. A couple of excellent examples of what we can accomplish with this technology are Snapchat’s Landmarker and Microsoft’s HoloLens. Consider the daily-used face filters on Instagram even if you haven’t been able to get your hands on Hololens or Landmarker yet. Or the enormously well-liked 2016 game Pokemon GO. These were all made possible by spatial computing.
5. Decentralization
The ideal configuration of the Metaverse would be the contrary of the OASIS of Ready Player One in which it was run by a one entity. Exploration and expansion are exponentially increased when the options are increased and technology is interoperable and constructed within competitive markets in which creators have the right to their own information and their own creations.
The decentralization process includes the blockchain, smart contracts, open-source platforms, and perhaps even a self-sovereign digital identity in the future. Distributed computing and microservices are increasingly making it possible for developers to access online resources through a scalable ecosystem.
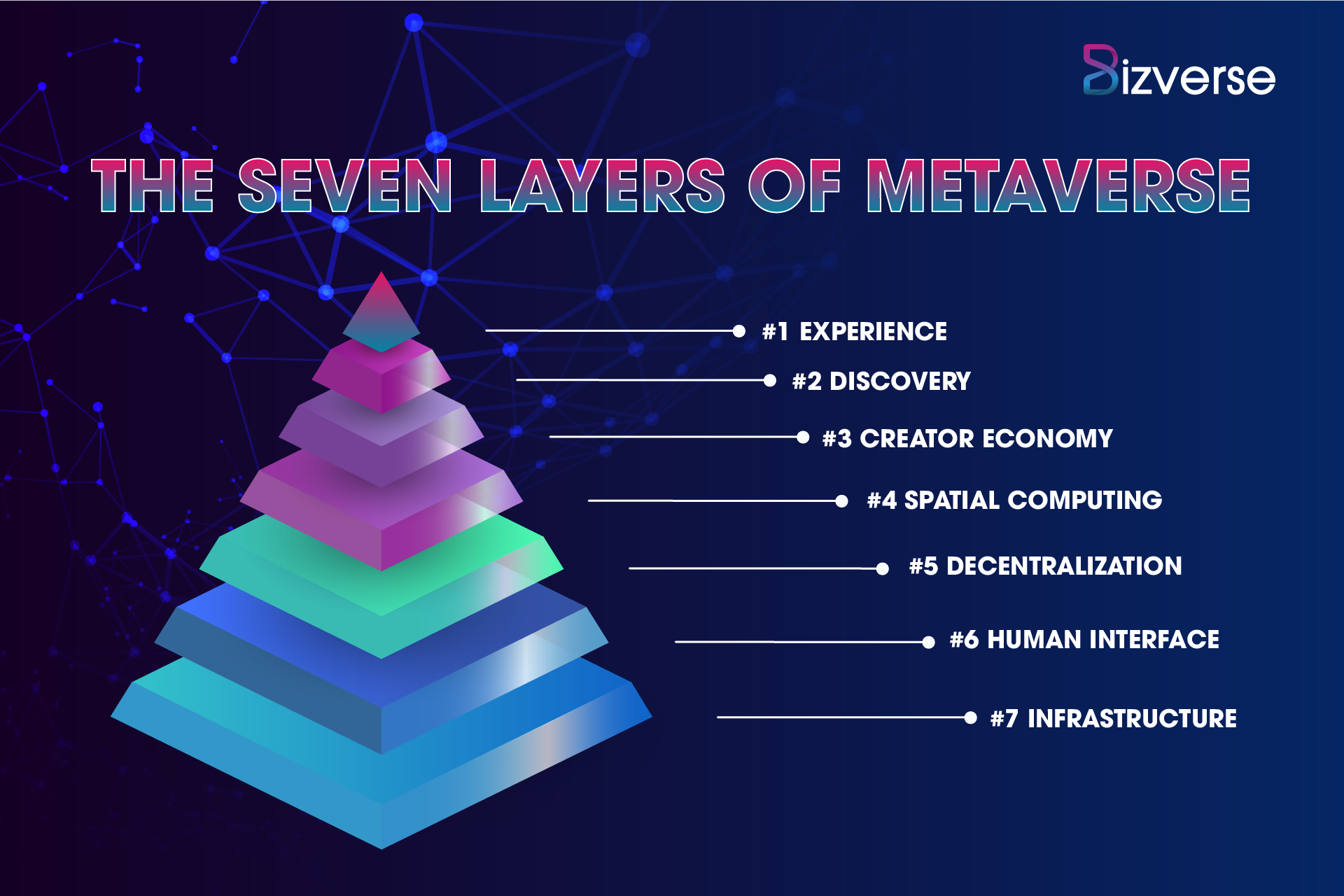
6. Human interface
Human intervention is a crucial component of the hardware layer of the metaverse. We’ll soon be able to learn about our surroundings, access maps, and even create shared AR experiences by simply glancing around at the real world thanks to the combination of spatial computing and human interface.
A well-known expert in technology and science studies named Donna Haraway wrote an essay titled “A Cyborg Manifesto” in 1985. The idea of the cyborg is employed in this article to reject the strict distinctions between “human” and “machine.” As technology becomes more compact and portable, it will move closer to our bodies, transforming us into cyborgs. With the help of smartwatches and smart glasses, we have already begun this process.
Additionally, research is already being done on neural interfaces between the brain and computers and biosensors. Therefore, haptics play a significant role in this layer as well. With this technology, even in the absence of things, information may be transmitted via touch.
7. Infrastructure
The technology that makes everything previously described a reality is part of the seventh layer. In the end, we need a technical infrastructure made up of 5G and 6G computing for all outer layers to exist. These will greatly increase bandwidth while lowering latency and network congestion.
Additionally, we require compact hardware that is potent in order for the devices specified in the human interference layer to function well. Radoff lists these as microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), which enable tiny sensors, semiconductors that are on the verge of 3nm processes, and compact, long-lasting batteries.
Although this seven-layered explanation is excellent for providing a general grasp, it appears that there is still much to be discovered about the metaverse. Naturally, we must first create the technology that will comprise the infrastructure. After then, it will be a matter of determining what functions and what doesn’t. One thing is certain, though: this new technology frontier will fundamentally alter the way we live and think.
